Are you looking to know How to Grow Glitter Bomb Weed Strain? then read this article to find out How to Grow Glitter Bomb Weed Strain?

INTRODUCTION
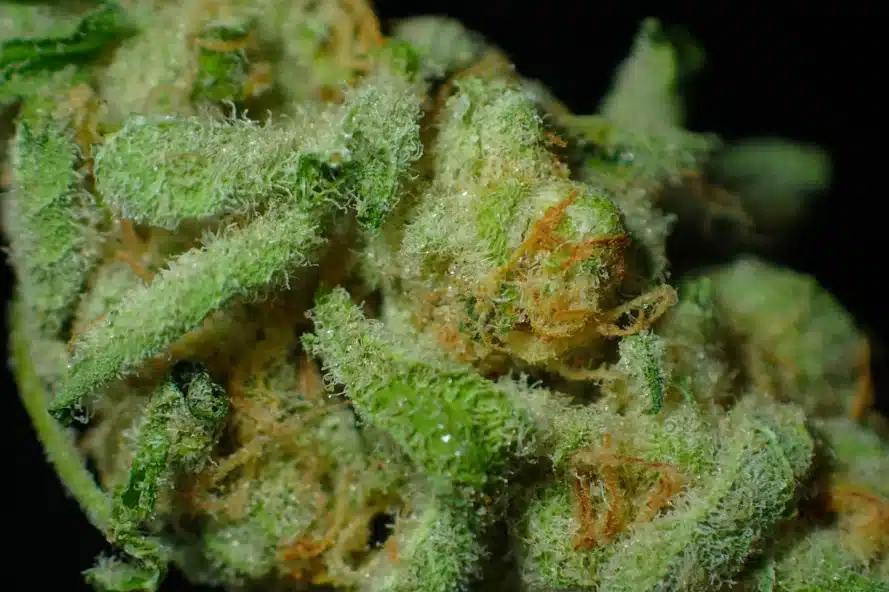
Glitter Bomb is an indica-leaning hybrid cannabis strain known for its strong but balanced effects. Users often experience a euphoric, uplifting mental high that can boost creativity, focus, and mood, while also feeling a calming body effect. Many people report relief from stress and anxiety, along with a general sense of relaxation. For some, the body high can be very sedating, sometimes causing couch-lock, which makes it ideal for evening use. This strain is also recognized for its attractive, frosty buds and high THC content, typically ranging from 22% to 28%. The glitter bomb strain is a cross of two well-known parent strains, offering a well-rounded experience that appeals to both recreational and medicinal users. Its buds are dense and covered in sparkling trichomes, giving it a glittery appearance. The aroma combines sweetness and earthiness, with subtle berry hints and skunky undertones. These flavors, paired with its balanced high, make Glitter Bomb enjoyable whether smoked or vaped.
GROWING GLITTER BOMB
The strain thrives in a temperate climate, with daytime temperatures between 70-80°F (21-27°C) and slightly cooler nights.
- Indoor Cultivation: Use high-quality LED or HPS lights. During the vegetative stage, provide 18-20 hours of light, then switch to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness for flowering. Good ventilation is essential, and reflective materials like Mylar can help distribute light evenly. Soil or hydroponic systems work well, but soil should be loose, well-draining, and pH-balanced between 6.0-6.5.
- Outdoor Cultivation: Choose a sunny location with well-draining soil enriched with organic matter. Protect plants from extreme weather and provide support for heavy buds. Proper spacing improves airflow and reduces the risk of mold.
PROPAGATION AND CARE
Start with high-quality feminized seeds. Germinate seeds in water or a damp paper towel until taproots appear. Transfer seedlings to small pots with light soil, maintaining warmth (75-80°F / 24-27°C) and 60-70% humidity. Gradually increase light as seedlings grow. Transplant to larger pots or final locations once true leaves develop.
During the vegetative stage, maintain 18-20 hours of light and provide nitrogen-rich nutrients for healthy foliage. Training techniques like low-stress training (LST) or topping help control plant height and improve bud exposure. In the flowering stage (8-10 weeks), reduce light to 12 hours, provide phosphorus and potassium-rich nutrients, and monitor temperature (65-75°F / 18-24°C) and humidity (40-50%). Use stakes or trellises to support heavy branches.
HARVESTING AND CURING
Harvest when trichomes are mostly milky with some amber for peak potency. Dry in a dark, ventilated space at 60-70°F (15-21°C) and 50-60% humidity. Trim buds and cure in airtight jars for 2-4 weeks, opening jars daily at first to release moisture. This process enhances flavor, smoothness, and overall quality.
Advantages: High THC, visually appealing buds, balanced effects, short flowering period, versatile use.
Challenges: Strong odour, heavy buds needing support, sensitive nutrient management, and potential pest issues.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Glitter Bomb is a versatile, visually stunning strain that delivers powerful effects and can be grown both indoors and outdoors with proper care.